16 March 2014
15 March 2014
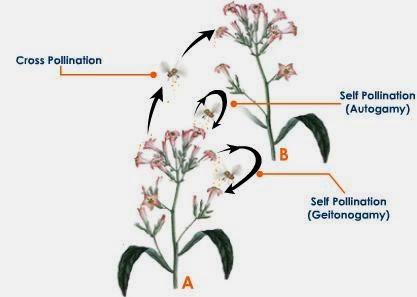
#108 Structure and functions of a flower
You need to be able to describe the structure and functions
of a named dicotyledonous (two seed leaves) flower.
14 March 2014
# 99 Urea formation, breakdown of alcohol & drugs in liver
 |
| Photo credit: James X - Biology Blog |
Surplus amino acids in the
bloodstream cannot be stored. They are removed by the liver and broken down
into the urea (which is the nitrogen-containing part of the amino acid) and a
sugar residue, which can be respired to release energy. The breakdown of amino
acids is called deamination.
11 March 2014
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)