- Carbohydrates: C, H, O
- Fats: C, H, O (lower O content than carbs)
- Proteins: C, H, O and N; sometimes S and P
1. Carbohydrates
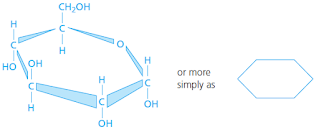 |
| one glucose molecule |
- monosaccharides: sugars with 1 carbon ring
- e.g.: fructose, glucose
- disaccharides: sugars with 2 carbon rings
- e.g.: maltose, sucrose
- polysaccharides: many glucose molecules joined together by chemical bonds
- glycogen: food storage in animal cells
- starch: food storage in plant cells
- cellulose: chains of glucose --> microscopic fibers --> form cell wall of plant cells
- formed from long chains of amino acids held together by chemical bonds
- C, H, N, O + P, S (chnops)
- 20 types of amino acids
- different sequences of amino acids give different shapes to protein molecules
- the shape and structure of proteins are specific to themselves, and is very important on its reaction with other substances
- active site of enzymes, is specific to its substrate
- binding site of antibodies, is specific to antigens (on pathogen)
- lipid in solid form = fat
- lipid in liquid form = oil
- C, H, O
|
Food tested |
Name of test |
Method |
Positive result |
|
Starch |
add a few drops of iodine to a solution
of food |
blue/black color |
|
|
Reducing sugar |
- add equal of amount of Benedict’s solution to solution of food - boil carefully over Bunsen flame |
a succession of color changes - turquoise à pale green à pea green à orange à brick red * the further the color change, the
more reducing sugar is present |
|
|
Protein |
- add equal amounts of NaOH to solution
of food à mix - add a few drops of 1% CuSO4;
no shaking! |
violet halo |
|
|
Fats |
- dissolve food in ethanol - pour solution into clean test tube |
milky white emulsion |
|
|
Vitamin C |
DCPIP test |
- DCPIP is a deep blue color - measure out 2.0 cm3
DCPIP into test tube - add fruit juice drop by drop,
counting shake mixture after each drop |
DCPIP decolorises |






No comments:
Post a Comment