A monohybrid cross involves the
crossing of individuals and the examination of one (mono) character
(flower colour, pod shape...) and different
(hybrid) traits (red colour, white colour) in their
offspring.
The Punnett square is a
useful tool for predicting the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring in a
genetic cross involving Mendelian traits.
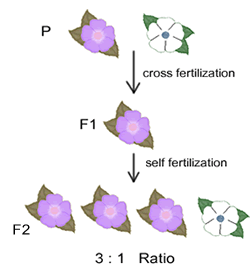
Mendel crossed true-breeding plants that differed for a given character. Pollen from true-breeding pea plants with purple flowers (one trait) was placed on stigmas of true-breeding plants with white flowers (another trait).
The F1 seeds were all
purple; the white flower trait failed to appear at all.
Because the purple flower
trait completely masks the white flower trait when true-breeding plants are
crossed, the purple flower trait is called dominant, and the white flower trait
is called recessive.
The F1 plants were allowed
to self-pollinate. This step was the monohybrid cross. (or the F1 cross). The progeny, called F2, were
examined: roughly 1/4 were white, and 3/4 were purple.
All the genetic crosses
shown below will involve examples using pea plants, which can be tall (T) of
dwarf (t) – tall is dominant to dwarf.
Examiner’s tips
- When you rite out a genetic cross, make sure you state what the symbols represents, e.g. T=tall, t=dwarf.
- Make sure you label each line in the cross (phenotype, genotype…).
- It’s a good idea to circle gametes to show that meiosis has happened.
- Read the question really carefully – are you asked to state the outcome in terms of the genotype or the phenotype?
Punnett square
1. A cross between a pure-breeding tall pea plant and
a pure-breeding dwarf pea plant.
As
tall is dominant to dwarf, and both plants are pure-breeding, their genotypes must be TT and tt.
2. A cross between two heterozygous tall pea plant.
The genotype of both plants must be Tt.
3. A cross between two heterozygous tall pea plant.
The hetetozygous tall pea plants must be Tt.
The dwarf pea plants must be tt.
Common misconceptions
Some students ignore the letters for alleles given in genetic questions
and make up their own, without stating a
key. This usually results in a number of marks being lost through errors that
could easily have been avoided.
Try this
1. In exam questions
involving genetic crosses, you often need to predict the genotypes of the
parents form descriptions of them. Work out the following genotypes, based on
peas that can be round or wrinkled, with round being dominate to wrinkled.
Remember that the dominant allele normally takes the capital letter or the
characteristic is represents
a) A heterozygous round pea [1 mark]
b) A wrinkled pea [1 mark]
c) A pure-breeding round pea
[1 mark]
Answer
a) Rr
b) rr
c) RR
2. Complete the passage by
writing the most appropriate word from the list in each space.
chromosome
diploid gene heterozygous
meiosis mutation phenotype
recessive dominant
Petal colour in pea plants
is controlled by a single ___which has two forms, red and white. The pollen grains
are produced by _____. After pollination, fertilization occurs and the
gametes join to form a ____ zygote.
When two red-flowered pea
plants were crossed with each other, some of the offspring were white-flowered.
The ____ of the rest of the offspring was red-flowered. The white-flowered form
is____ to the red-flowered form and each of the parent plants was therefore_____. [6 marks]
Answer
gene meiosis diploid
phenotype recessive
heterozygous




Your Punnett squares video doesnt work. "This video is private"
ReplyDeleteThanks. I removed it.
DeleteIt is very helpful.
ReplyDelete